The WHO's "Prequalification" and "Emergency Use Listing" Racket
Are products that are approved, "Prequalified" or listed for emergency use (EUL) by the World Health Organization truly "safe and effective," or is this just another corrupt, money-making racket?
Are you aware that the World Health Organization has “prequalified” 272 vaccines? They charge over $100,000 per vaccine!
In order for “health related products” to be part of the United Nations procurement system, they must be “prequalified” by the WHO, which charges substantial one-time and ongoing fees in return for their “prequalification.”
A “racket” is defined as the act of creating demand for a “service” through extortion or intimidation when such a “service” would not have been needed otherwise.
A “racketeer” is a person who engages in organized criminal activity, typically for financial gain.
“Racketeering” is a type of organized crime in which the perpetrators set up a coercive, fraudulent, extortionary, or otherwise coordinated scheme or operation (a "racket") to repeatedly or consistently collect a profit.
Is the WHO ethically and financially liable for the harm that results from the products that they “prequalify?”
Or does their money-making scheme enable them to create an illusion of safety and effectiveness while redirecting blame to the Responsible National Regulatory Agencies?
Click on the links below for details:
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/fees-prequalification
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/prequalified-vaccines
CLICK HERE to download the CSV data file.
If manufacturers want their products to be eligible for procurement by United Nations agencies, they must submit to the World Health Organization’s scheme to have their products “prequalified.”
The proposed “Pandemic Agreement” would require nations to support the World Health Organization’s growing influence over the approval process for vaccines, immunization devices, [catalog] drugs, in vitro diagnostics, inspection services, vector control products and yes, even male circumcision devices.
Article 14.5
Each Party shall, as appropriate and consistent with applicable law, encourage relevant developers and manufacturers of pandemic related health products to diligently seek regulatory authorizations and approvals from national and/or regional regulatory authorities, including WHO listed authorities, and prequalification of such products by WHO.
Annex 6 of the International Health Regulations already states:
1. Vaccines and prophylaxis designated by WHO shall be subject to its approval.
3. Certificates under this Annex are valid only if the vaccine or prophylaxis used has been approved by WHO.
https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/wha77/a77_aconf14-en.pdf
The World Health Organization charges manufacturing companies a lot of money to have their products “prequalified.”
WHO prequalification activities were long funded by international donors through short-term grants.
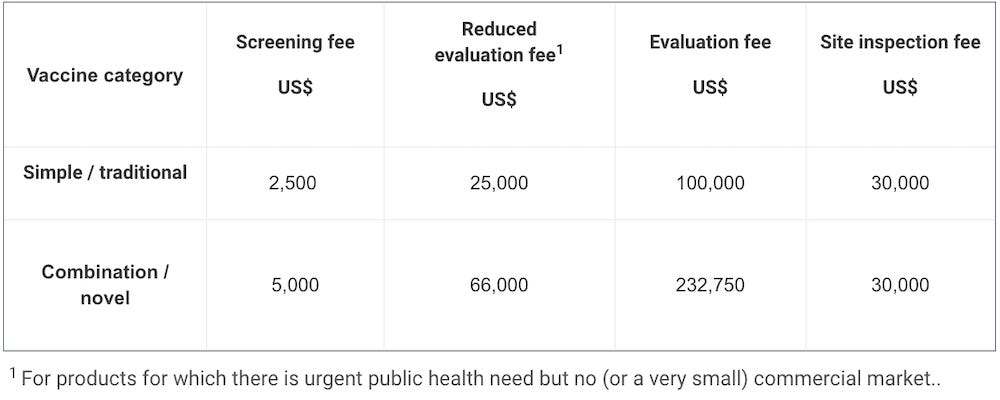
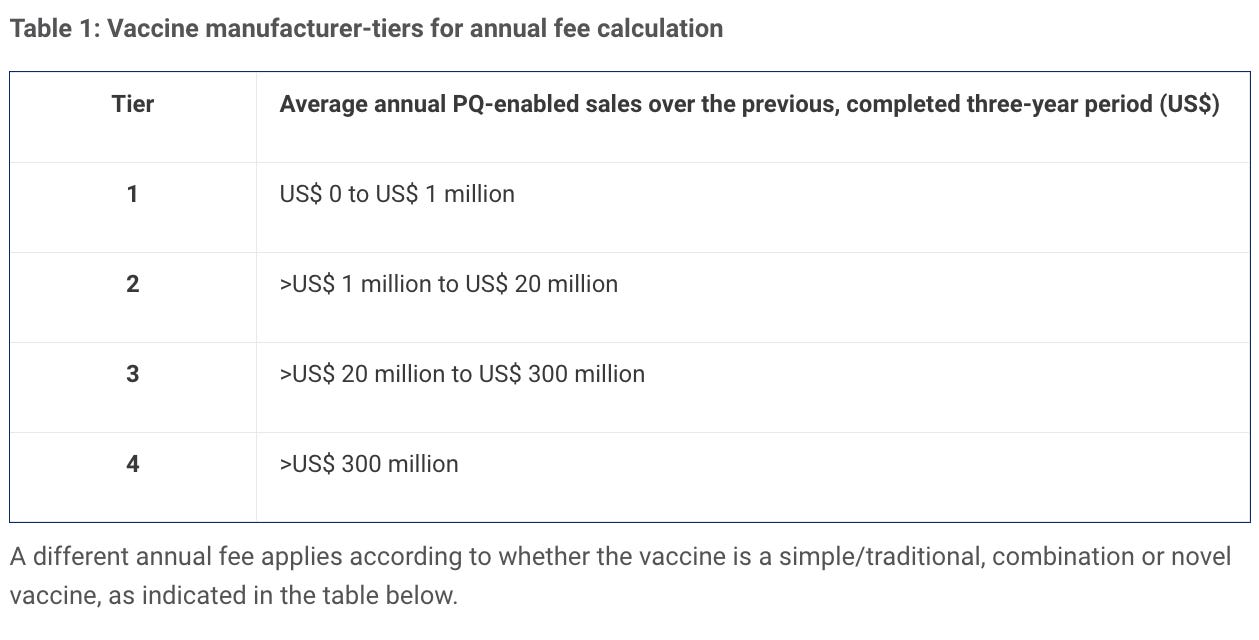
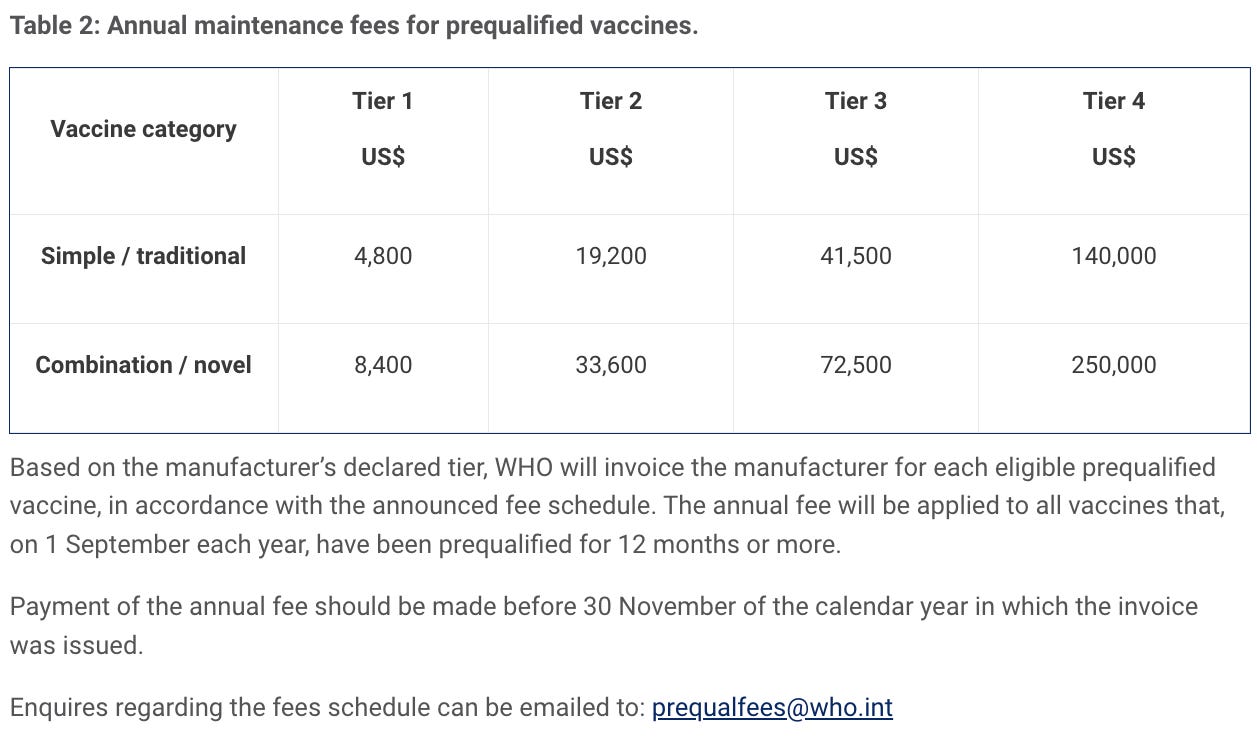
In January 2017 therefore introduced a new fee model for medicines — finished pharmaceutical products (FPPs) and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) — and vaccines, and later for in vitro diagnostics (IVDs), in August 2018.
In 2023, the WHO’s “Fee for Services Fund” made a profit of $14.8 million on the $27.8 million in fees that they collected.
Fee for Services Fund
This fund was established to record, and report fees charged to manufacturers for prequalification services to assess the quality, safety and efficacy of medical products (vaccines, medicines or diagnostics). (page 59)
(Page 96)
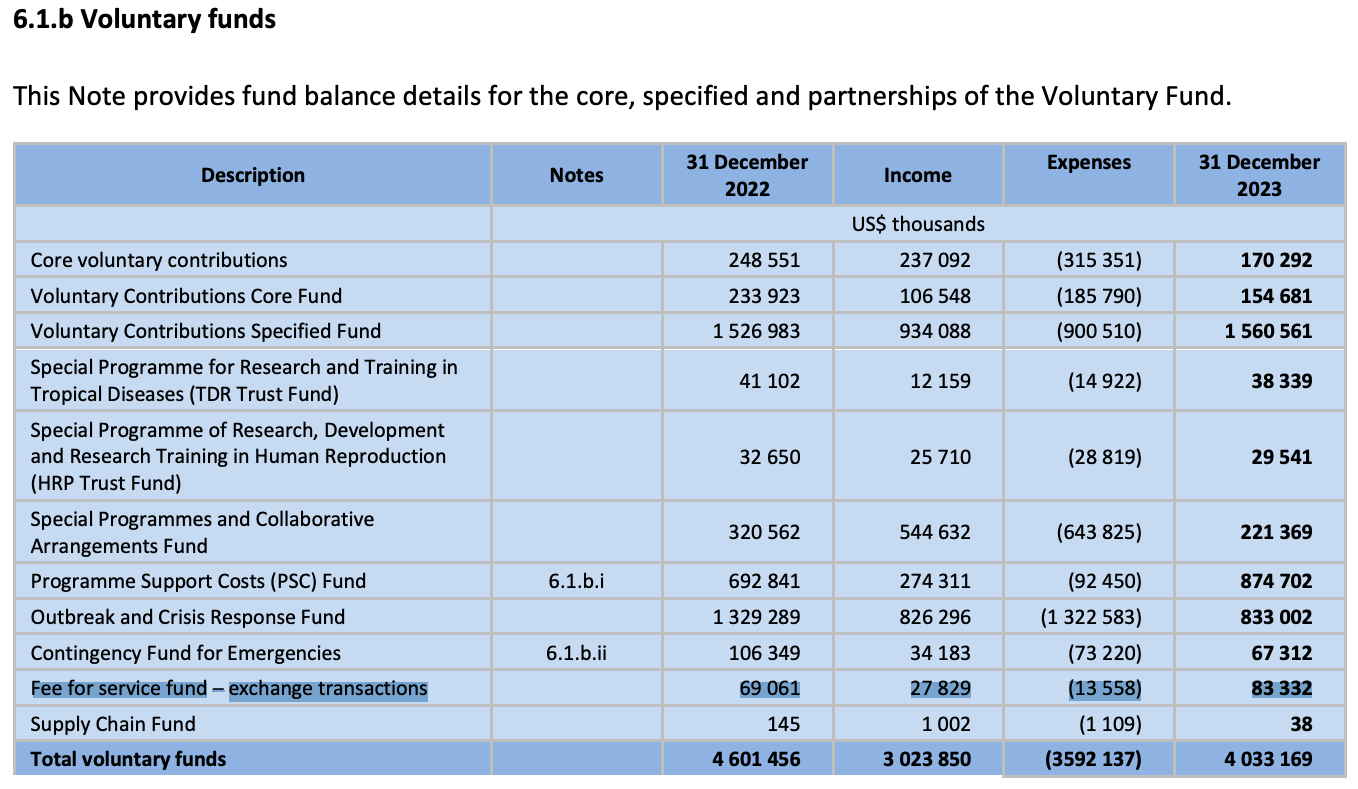
VACCINES
PreQualification Fees:
Screening of an application
Dossier evaluation
Site inspection
Annual maintenance
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/fees-prequalification
If a vaccine has undergone thorough evaluation of relevant data, testing of samples and WHO inspection of relevant manufacturing sites — and the outcome is positive — it is included in the WHO List of Prequalified Vaccines. This means that it: meets WHO standard for vaccine quality, safety and efficacy standards, as endorsed by the WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization (ECBS).
The aforementioned recommended standards include independent and appropriate regulatory oversight of the vaccine by the responsible, functional national regulatory authority (NRA).
WHO cannot represent that the listed vaccines and manufacturing sites will continue to meet the aforesaid standards and/or operational specifications.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/list-prequalified-vaccines
The process by which standards and norms are evaluated by the WHO for the prequalification of vaccines is NOT subject to public input or scrutiny.
WHO vaccines prequalification applies WHO-established vaccine standards, norms and other recommendations as they become available. These include standards and norms developed and adopted by the WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization and which cover vaccine standards that address the manufacturing, licensing, quality control, labelling, transportation and storage of vaccines.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/what-standards-are-applied-vaccines-prequalification
IMMUNIZATION DEVICES
How much does it cost to get an immunization device prequalified?
WHO recuperates the cost of dossier evaluation through fees charged to the manufacturer. Dossier evaluation fees are set per category of immunization products or devices and range between $2,000 and $3,200 per category, with the exception of coolant packs, for which the application fee is $600.
Manufacturers whose products are successfully prequalified by WHO will also be charged a fee for the annual product review of each prequalified product. Annual review fees are also set per category of product and range from $1,200 to $1,600, with the exception of coolant packs, for which the annual review fee is $300.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/how-much-does-it-cost-get-immunization-device-prequalified
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/immunization-devices/product-categories
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/immunization-devices/download-catalogue
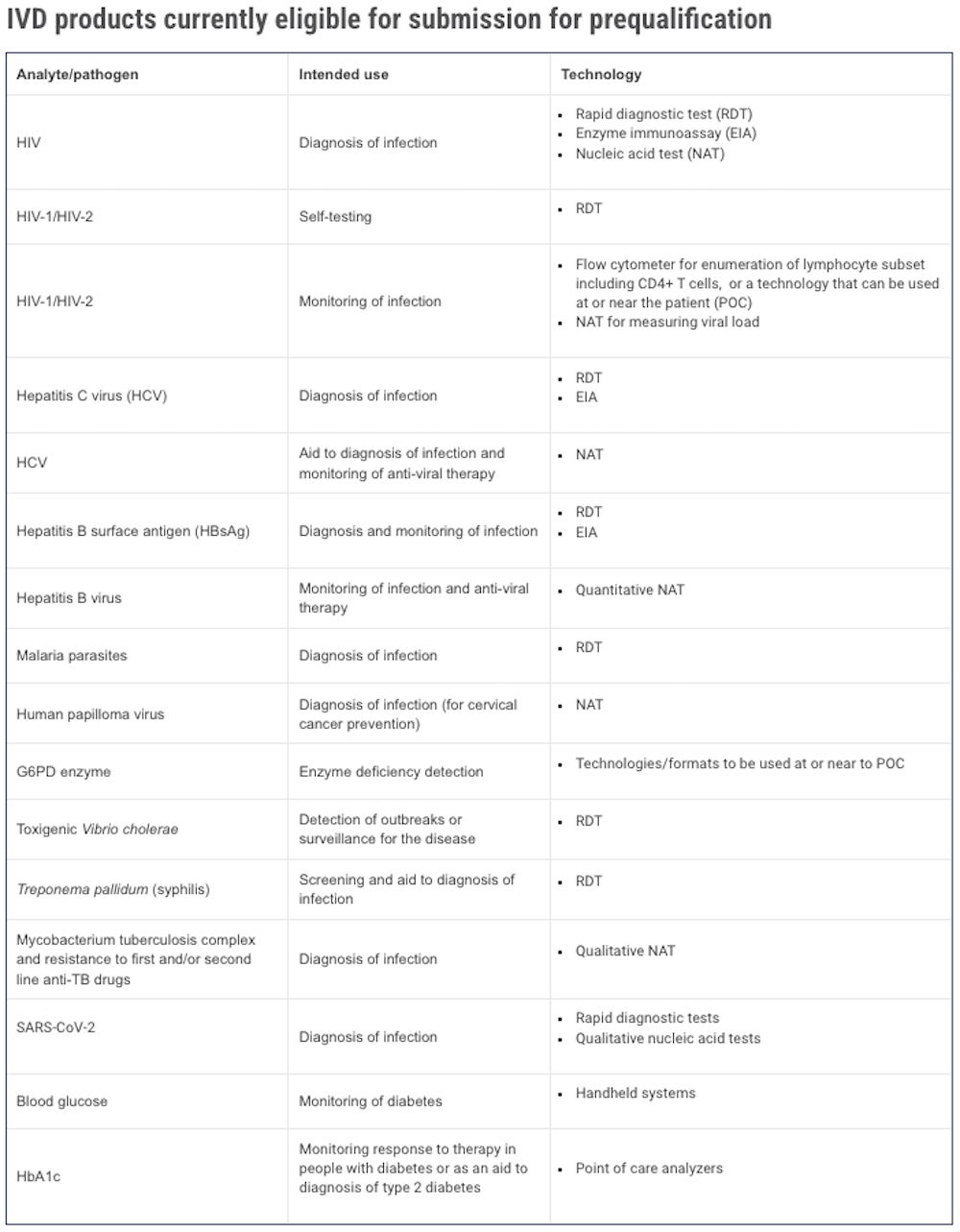
IN-VITRO DIAGNOSTICS
Prequalification fees
Prequalification fees are levied to cover part of the costs associated with product dossier screening and review, performance evaluation commissioned by WHO, manufacturing site(s) inspection, review of labelling, dissemination of prequalification information, change assessment and dissemination of change information.
Fees must paid within a defined timeline. Failure to do so will result in cancellation of the assessment application, or change request application, or suspension of prequalification status of the prequalified product, whichever is applicable. Fees are non-refundable.
Payment of prequalification fees does not guarantee that the product will be prequalified and/or that, if prequalified, the product will retain its prequalification status for any minimum duration.
Assessment fee
A prequalification assessment fee is charged to a manufacturer once its application has been determined to be eligible for WHO prequalification assessment. For a product undergoing full assessment, US$ 5000 is charged for dossier screening and US$ 12,000 for product assessment. For a product undergoing abridged assessment the fee is US$ 8000.
Change assessment fee
WHO will review the change documentation submitted by the manufacturer to determine the type and level of assessment required which, in turn, will determine whether the change assessment fee of US$ 3000 will be charged. The change assessment fee is waived in certain cases. WHO does not charge fees for the assessment of administrative changes and for certain abridged reviews. WHO determines the applicability of a waiver on a case-by-case basis.
Annual fee
An annual fee of US$ 4000 is levied for each product listed on the WHO List of Prequalified In Vitro Diagnostics. An invoice for the annual fee will be issued by WHO to the manufacturer on or before 1 October of each year. The annual fee is applicable to all IVDs that, by 1 September of that year, have been listed for 12 months or more. Payment of the annual fee must be made before 30 November of the calendar year in which the invoice is issued.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vitro-diagnostics/vitro-diagnostics-eligible-who-prequalification
MEDICINES
How much does medicines prequalification cost?
Fees are levied for evaluation for prequalification for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished pharmaceutical product (FPPs), and for evaluation of major variations for prequalified FPPs. An annual fee is also levied for each prequalified API or FPP. In some instances, deferred fees may be applied.
In considering an application for prequalification evaluation, manufacturers should also consider the common expenses involved in preparing a product for WHO or other stringent evaluation.
The majority of quality control laboratories (QCLs) that WHO prequalifies are national laboratories or academic institutions, the financial resources of which are often limited. WHO therefore decided not to levy a fee for QCL prequalification.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/how-much-does-medicines-prequalification-cost
Emergency Use Listing (EUL)
The WHO Emergency Use Listing Procedure (EUL) is a risk-based procedure for assessing and listing unlicensed vaccines, therapeutics and in vitro diagnostics with the ultimate aim of expediting the availability of these products to people affected by a public health emergency.
Evaluation will determine whether, in light of available WHO/international standards, the submitted data demonstrate a reasonable likelihood that the vaccine quality, safety and effectiveness are acceptable and that the benefits outweigh the foreseeable risks and uncertainties in the context of a PHEIC.
If quality and/or safety issues are identified post listing, WHO may seek advice from the Technical Advisory Group for emergency use listing (TAG EUL)
All submitted information will be assessed to determine whether the vaccine’s benefit‒risk ratio remains positive.
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/emergency-use-listing-procedure
How is the EUL procedure different from Prequalification?
The EUL is a special procedure for unlicensed vaccines, medicines and in vitro diagnostics in the event of a public health emergency when the community/public health authorities may be willing to tolerate less certainty about the efficacy and safety of products, given the morbidity and/or mortality of the disease and the lack or paucity of treatment, diagnosis/detection or prevention options. The procedure is intended to provide a time-limited listing for unlicensed products in an emergency context when limited data are available and the products are not yet ready for application for prequalification. As part of the EUL, the expectation is that the manufacturer will complete the development of the product and submit for licensure and WHO prequalification.
Does the listing of a product assessed under the EUL procedure ensure safety, efficacy & performance of the product?
The assessment of products under the EUL procedure is conducted on the quality, safety, efficacy or performance data available up to the time of submission. However, since the product is still in development (vaccines and medicines only, IVDs under development are not accepted for assessment), the decision to list will be based on a risk-benefit assessment considering the public health emergency. The available data must provide an indication that the use of the product will provide a benefit to the target population.
What written standards are used to assess new products if there are no published guidelines for the specific product?
The product evaluation committee will prepare a list of existing guidelines that are related to the vaccines and medicines, and published scientific data that may support the evaluation. This list of documents used as reference will be included in the report prepared by the product evaluation committee
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/sites/default/files/document_files/QA-EUL-General_July-2020.pdf
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/
Male Circumcision Devices
Prequalification fees
Prequalification fees are levied to cover part of the costs associated with product dossier screening and review, manufacturing site(s) inspection, review of labelling, dissemination of prequalification information, change assessment and dissemination of change information.
Fees must paid within a defined timeline. Failure to do so will result in cancellation of the assessment application, or change request application, or suspension of prequalification status of the prequalified product, whichever is applicable. Fees are non-refundable.
Payment of prequalification fees does not guarantee that the product will be prequalified and/or that, if prequalified, the product will retain its prequalification status for any minimum duration.
Assessment fee
A prequalification assessment fee is charged to a manufacturer once its application has been determined to be eligible for WHO prequalification assessment, as follows: US$ 5000 for dossier screening and US$ 12,000 for product assessment.
Change assessment fee
WHO will review the change documentation submitted by the manufacturer to determine the type and level of assessment required which, in turn, will determine whether the change assessment fee of US$ 3000 will be charged. The change assessment fee is waived in certain cases. WHO determines the applicability of a waiver on a case-by-case basis.
Payment of the change assessment fee does not, however, guarantee that the change will be accepted by WHO.
Annual fee
An annual fee of US$ 4000 is levied for each product listed on the WHO List of Prequalified MCDs. An invoice for the annual fee will be issued by WHO to the manufacturer on or before 1 October of each year. The annual fee is applicable to all IVDs that, by 1 September of that year, have been listed for 12 months or more. Payment of the annual fee must be made before 30 November of the calendar year in which the invoice is issued.
OVERVIEW OF THE WHO PREQUALIFICATION OF MALE CIRCUMCISION DEVICES
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/330040/WHO-MVA-EMP-RHT-PQT-2019.02-eng.pdf?sequence=1
SOURCES:
Regulation and Prequalification Emergency use listing
Home | WHO - Prequalification of Medical Products (IVDs, Medicines, Vaccines and Immunization Devices, Vector Control)
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/
FAQs
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq
Regulation and Prequalification
https://www.who.int/teams/regulation-prequalification/overview
Fees for prequalification
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/fees-prequalification
Prequalified Vaccines
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/prequalified-vaccines
Vaccines Eligible for WHO Prequalification
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/vaccines-eligible-who-prequalification
Prequalification Procedures and Fees: Vaccines
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/prequalification-procedures-and-fees-vaccines
What is the duration and cost of vaccines prequalification?
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/what-duration-and-cost-vaccines-prequalification
How much does it cost to get an immunization device prequalified?
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/how-much-does-it-cost-get-immunization-device-prequalified
How much does medicines prequalification cost?
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/how-much-does-medicines-prequalification-cost
What standards are applied for vaccines prequalification?
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/faq/what-standards-are-applied-vaccines-prequalification
Emergency Use Listing Procedure
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/emergency-use-listing-procedure
In Vitro Diagnostics Manufacturers
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vitro-diagnostics/manufacturers
Cost of WHO Immunization Devices prequalification
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/immunization-devices/cost-who-immunization-devices-prequalification
Immunization Devices Product categories
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/immunization-devices/product-categories
Prequalification Procedures and Fees: Immunization Devices
Prequalification Procedures and Fees: In Vitro Diagnostics
Prequalified In Vitro Diagnostics
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vitro-diagnostics/prequalified-vitro-diagnostics
Funding
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/about/funding
Laboratories
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/inspection-services/laboratories
Documents A to Z
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/key-resources/documents/inspection-services
What We Do
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/inspection-services/what-we-do
News
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/news
Post-prequalification Obligations & Commitments
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/immunization-devices/post-prequalification-obligations-commitments
Welcome to Inspection Services
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/inspection-services/welcome-inspection-services
History and Mission of WHO Prequalification
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/about
eCTD Portal
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/ectd-portal
Prequalified Vaccine Annual Report (PQVAR)
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/prequalified-vaccine-annual-report-pqvar
WHO Prequalification - Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/about/who-prequalification-key-performance-indicators-kpis
Emergency Use Listing Procedure - Vaccines
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/vaccines/emergency-use-listing-procedure
Q&A for Guidelines on Emergency Use Listing Procedure
https://extranet.who.int/prequal/sites/default/files/document_files/QA-EUL-General_July-2020.pdf
A quiet revolution in global public health: The World Health Organization’s Prequalification of Medicines Programme | Journal of Public Health Policy
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/jphp.2013.53
Delivering Quality-Assured medical products for all - 2019–2023
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MVP-RHT-2019.01
OVERVIEW OF THE WHO PREQUALIFICATION OF MALE CIRCUMCISION DEVICES
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/330040/WHO-MVA-EMP-RHT-PQT-2019.02-eng.pdf?sequence=1
310-619-3055
JamesRoguski.substack.com/archive
All content is free to all readers.
All support is deeply appreciated.



















Let’s start a pool, “On what day after January 20, 2025 will President Trump withdraw the USA from the WHO?”
I’ll start: January 26, 2025
James, this is one of your most important posts. Your research and points are impeccable.
All Health entities are compromised.
Hospitals get $13-39k to diagnose and treat patients having "Covid".
Fema is still paying families $9k for "Covid" deaths.
And crisis level turbo cancers caused by "Covid" gene therapy bioweapon SV40 Plasmid DNA contamination are being explained away as new found malevolent DNA inherent defect we all have lurking within.
We are being murdered by laboratory, boardroom, govt psychopaths.
PROBLEM:
Feb 2024
By 2050, worldwide cancer rates expected to nearly DOUBLE, says the WHO
https://www.newstarget.com/2024-02-22-2050-worldwide-cancer-rates-to-nearly-double.html
SOLUTION:
Nov 6 2024
Study raises hopes of treating aggressive cancers by zapping rogue DNA
Tumours could be reduced by targeting genetic material driving their growth with a new drug in early-stage trials
Ian Sample Science editor
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2024/nov/06/zapping-rogue-dna-key-treating-aggressive-cancers-study